来源:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411d7Ys?t=3&p=13
RNN_Classifier model
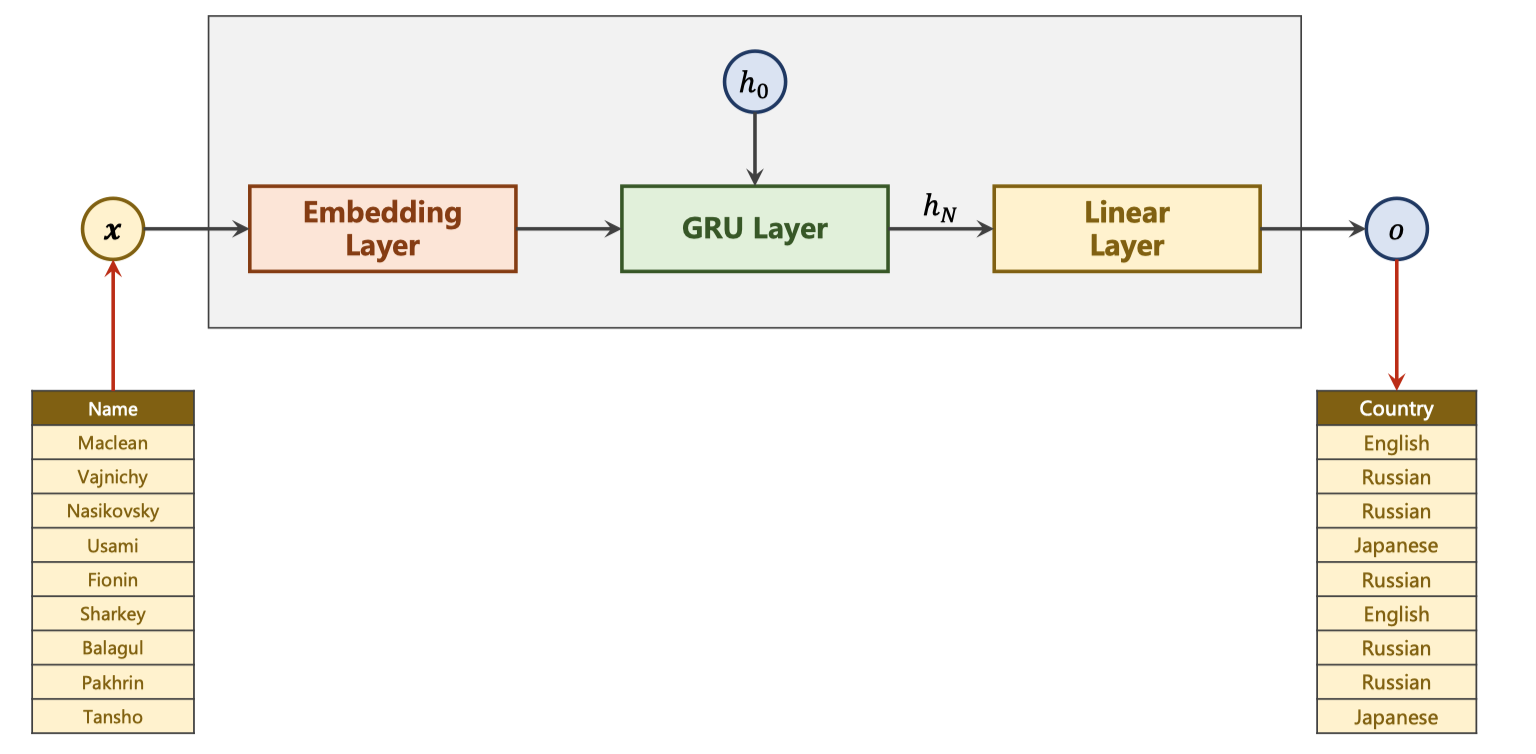
1. 准备数据
对于每个名字需要得到一个向量
通过ASCII对于每个名字的每个字符都得到一个
one-hot vector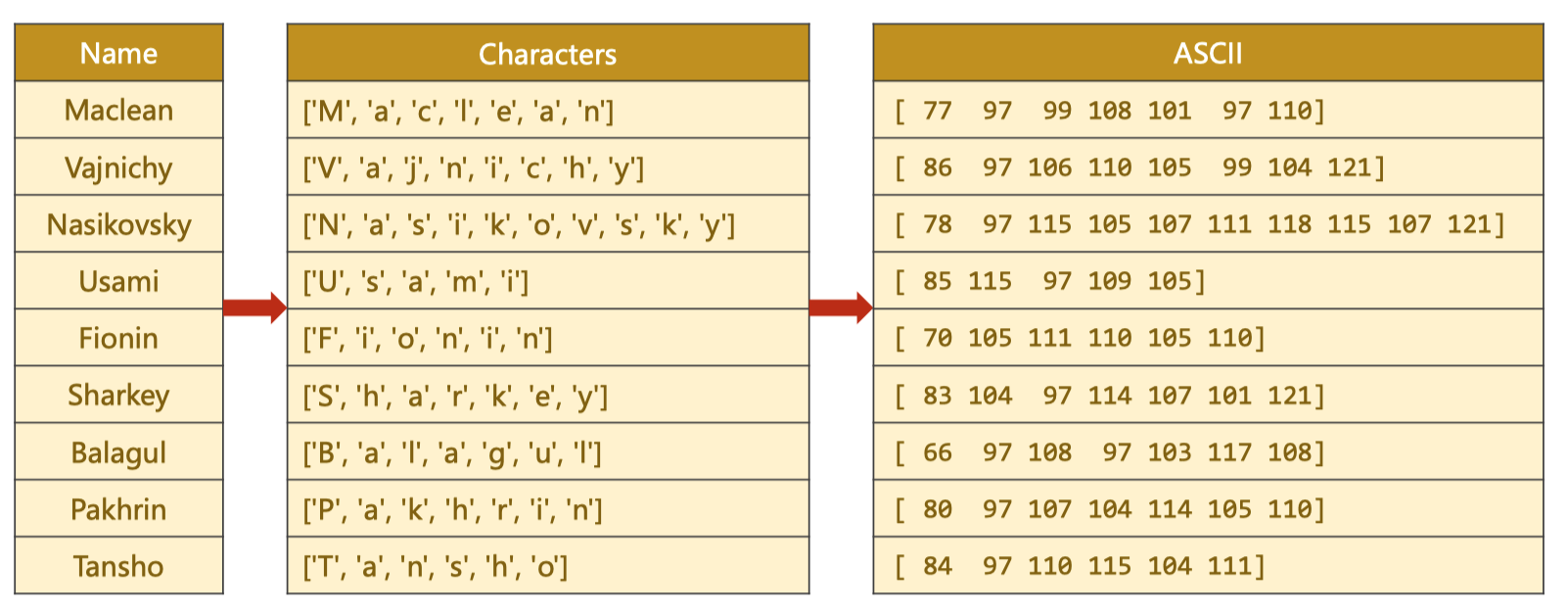
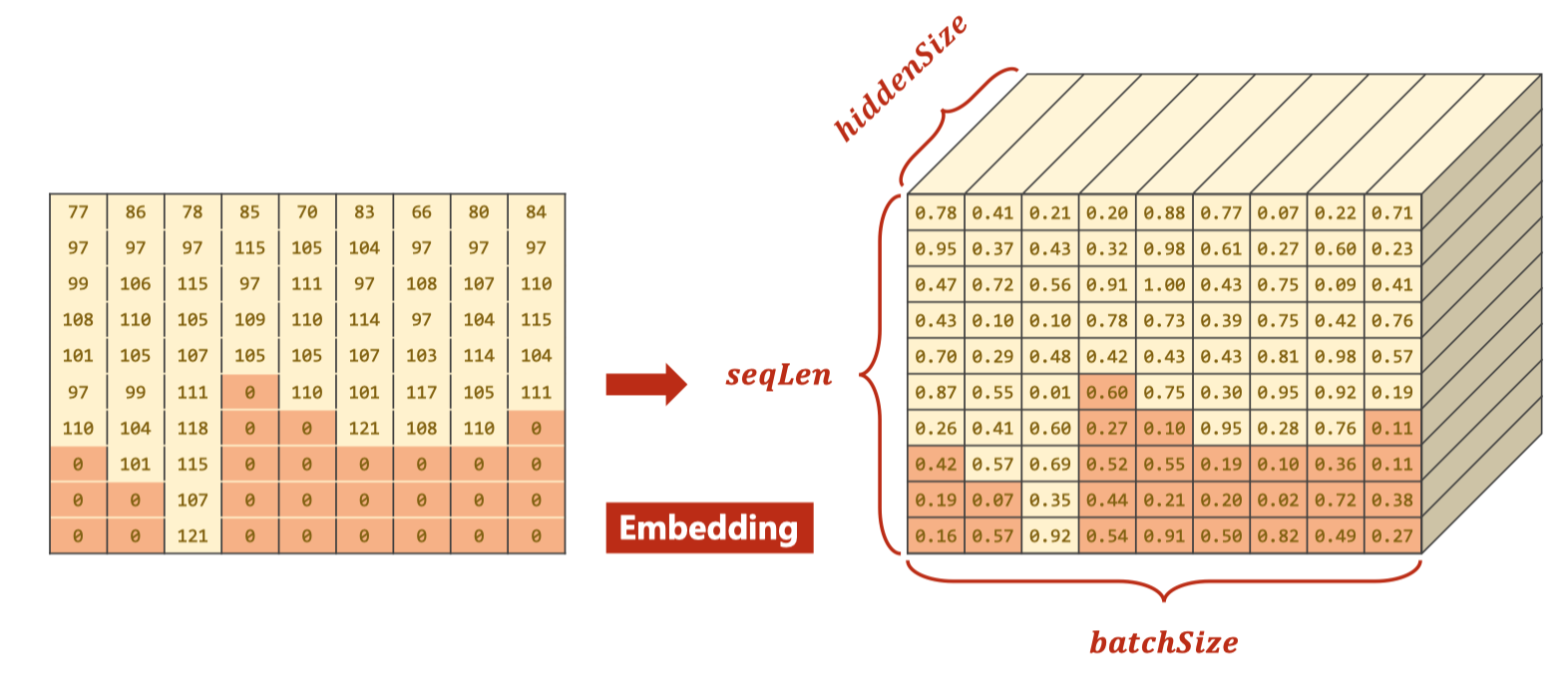
由于输入是矩阵所以需要
padding
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import gzip
import csv
class NameDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, is_train_set):
filename = './names_train.csv.gz' if is_train_set else './names_test.csv.gz'
with gzip.open(filename, 'rt') as f: # r表示只读,从文件头开始 t表示文本模式
reader = csv.reader(f)
rows = list(reader)
self.names = [row[0] for row in rows]
self.len = len(self.names)
self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows]
self.country_list = list(sorted(set(self.countries)))
self.country_dict = self.getCountryDict()
self.country_num = len(self.country_list)
def __getitem__(self, index): # 根据索引拿到的是 名字,国家的索引
return self.names[index], self.country_dict[self.countries[index]]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
def getCountryDict(self):
country_dict = dict()
for idx, country_name in enumerate(self.country_list, 0):
country_dict[country_name] = idx
return country_dict
def idx2country(self, index):
return self.country_list[index]
def getCountriesNum(self):
return self.country_num
HIDDEN_SIZE = 100
BATCH_SIZE = 256
N_LAYER = 2
N_EPOCHS = 50
N_CHARS = 128 # 这个是为了构造嵌入层
trainSet = NameDataset(is_train_set=True)
trainLoader = DataLoader(trainSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
testSet = NameDataset(is_train_set=False)
testLoader = DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False)
N_COUNTRY = trainSet.getCountriesNum()2. 构建模型
GRU的维度
- 输入维度
- 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡: (𝑠𝑒𝑞𝐿𝑒𝑛, 𝑏𝑎𝑡𝑐ℎ𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒, ℎ𝑖𝑑𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒)
- hidden: (nLayers * nDirections, batchSize, hiddenSize)
- 输出维度
- output: (seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize * nDirections)
- hidden: (nLayers * nDirections, batchSize, hiddenSize)
- 示意图
GRU处理时可以使用pack_padded_sequence提高效率
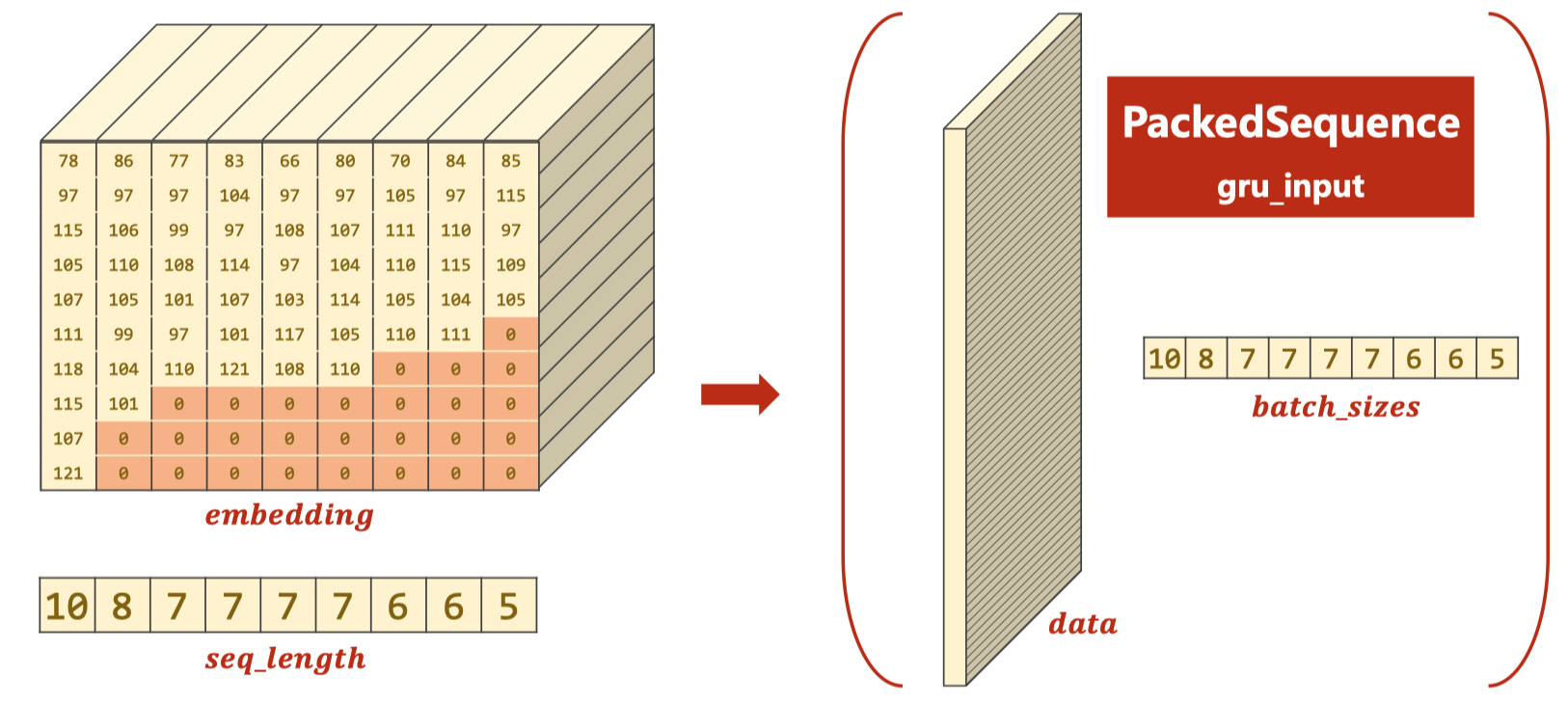
class RNNClassifier(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, bidirectional=True):
super(RNNClassifier, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.n_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1 # 使用双向的GRU
# 嵌入层(𝑠𝑒𝑞𝐿𝑒𝑛, 𝑏𝑎𝑡𝑐ℎ𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒) --> (𝑠𝑒𝑞𝐿𝑒𝑛, 𝑏𝑎𝑡𝑐ℎ𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒, hidden_size)
self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = torch.nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, bidirectional=bidirectional)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size * self.n_directions, output_size)
def _init_hidden(self, batch_size):
hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers * self.n_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size)
return hidden
def forward(self, input, seq_lengths):
# input shape : B x S -> S x B
input = input.t()
batch_size = input.size(1)
hidden = self._init_hidden(batch_size)
embedding = self.embedding(input)
# pack them up
gru_input = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence(embedding, seq_lengths)
output, hidden = self.gru(gru_input, hidden)
if self.n_directions == 2:
hidden_cat = torch.cat([hidden[-1], hidden[-2]], dim=1)
else:
hidden_cat = hidden[-1]
fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat)
return fc_output
3. 数据转化成Tensor
def name2list(name):
arr = [ord(c) for c in name]
return arr, len(arr)
def make_tensors(names, countries):
sequences_and_lengths = [name2list(name) for name in names]
name_sequences = [s1[0] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths]
seq_lengths = torch.LongTensor([s1[1] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths])
countries = countries.long()
# make tensor of name, BatchSize * seqLen
# 他这里补零的方式先将所有的0 Tensor给初始化出来,然后在每行前面填充每个名字
seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences), seq_lengths.max()).long()
# print("seq_lengths.max:", seq_lengths.max())
for idx, (seq, seq_len) in enumerate(zip(name_sequences, seq_lengths), 0):
seq_tensor[idx, :seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq)
# sort by length to use pack_padded_sequence
# 将名字长度降序排列,并且返回降序之后的长度在原tensor中的小标perm_idx
seq_lengths, perm_idx = seq_lengths.sort(dim=0, descending=True)
# 这个Tensor中的类似于列表中切片的方法神奇啊,直接返回下标对应的元素,相等于排序了
seq_tensor = seq_tensor[perm_idx]
countries = countries[perm_idx]
# 返回排序之后名字Tensor,排序之后的名字长度Tensor,排序之后的国家名字Tensor
return seq_tensor, seq_lengths, countries4. 训练数据
classifier = RNNClassifier(N_CHARS, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_COUNTRY, N_LAYER)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=0.001)
import time
import math
def trainModel():
def time_since(since):
s = time.time() - since
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
total_loss = 0
for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(trainLoader, 1):
# print(type(names), type(countries))
# print(len(names), countries.shape)
inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries)
output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths)
# print("Shape:", output.shape, target.shape)
# 注意输出和目标的维度:Shape: torch.Size([256, 18]) torch.Size([256])
loss = criterion(output, target)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if i % 10 == 0:
print(f'[{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch} ', end='')
print(f'[{i * len(inputs)}/{len(trainSet)}] ', end='')
print(f'loss={total_loss / (i * len(inputs))}')
return total_loss
def testModel():
correct = 0
total = len(testSet)
print("evaluating trained model ... ")
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(testLoader):
inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries)
output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths)
# 注意这个keepdim的使用,为了直接和target计算loss
pred = output.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)[1]
# 注意这个view_as 和 eq
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
percent = '%.2f' % (100 * correct / total)
print(f'Test set: Accuracy {correct}/{total} {percent}%')
return correct / total
N_EPOCHS = 50
start = time.time()
print("Training for %d epochs..." % N_EPOCHS)
acc_list = []
for epoch in range(1, N_EPOCHS + 1):
# Train cycle
trainModel()
acc = testModel()
acc_list.append(acc)训练结果:
Training for 50 epochs... [0m 2s] Epoch 1 [2560/13374] loss=0.00895661092363298 [0m 4s] Epoch 1 [5120/13374] loss=0.007739758561365306 [0m 6s] Epoch 1 [7680/13374] loss=0.0069853457777450485 [0m 8s] Epoch 1 [10240/13374] loss=0.006530495395418256 [0m 11s] Epoch 1 [12800/13374] loss=0.006135637713596225 evaluating trained model ... Test set: Accuracy 4535/6700 67.69% [0m 15s] Epoch 2 [2560/13374] loss=0.004228085093200207 [0m 17s] Epoch 2 [5120/13374] loss=0.0041014277492649855 [0m 19s] Epoch 2 [7680/13374] loss=0.004011582878107826 [0m 22s] Epoch 2 [10240/13374] loss=0.0038964587613008915 [0m 24s] Epoch 2 [12800/13374] loss=0.0038181920163333416 evaluating trained model ... ......(中间省略若干) [12m 46s] Epoch 49 [2560/13374] loss=0.00016357196727767587 [12m 49s] Epoch 49 [5120/13374] loss=0.0001682748734310735 [12m 51s] Epoch 49 [7680/13374] loss=0.00017566338913942067 [12m 54s] Epoch 49 [10240/13374] loss=0.0001776946208337904 [12m 57s] Epoch 49 [12800/13374] loss=0.00018831568930181676 evaluating trained model ... Test set: Accuracy 5627/6700 83.99% [13m 2s] Epoch 50 [2560/13374] loss=0.00016892087151063607 [13m 5s] Epoch 50 [5120/13374] loss=0.00015529338124906645 [13m 7s] Epoch 50 [7680/13374] loss=0.00017500294488854707 [13m 11s] Epoch 50 [10240/13374] loss=0.00017692927776806754 [13m 14s] Epoch 50 [12800/13374] loss=0.00018558732335804962 evaluating trained model ... Test set: Accuracy 5613/6700 83.78%
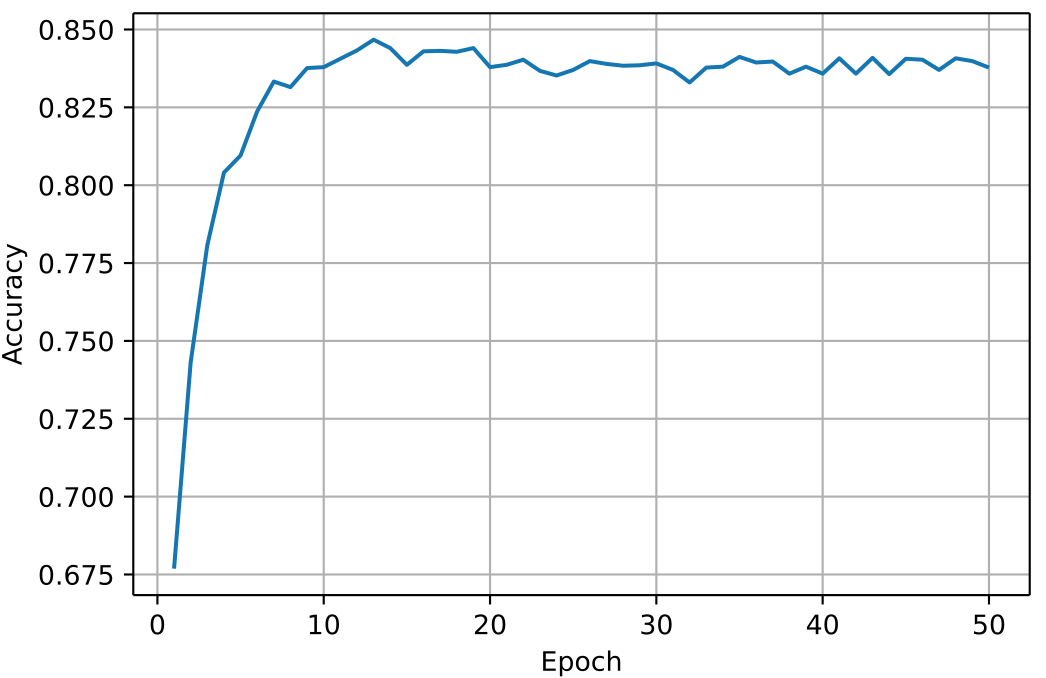
5. 可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
epoch = np.arange(1, len(acc_list) + 1)
acc_list = np.array(acc_list)
plt.plot(epoch, acc_list)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.show()