Pytorch for RNN
来源:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411d7Ys?p=12
How to use RNNCell
注意几个参数
输入和隐层(输出)维度
序列长度
批处理大小
- 注 调用RNNCell这个需要循环,循环长度就是序列长度
import torch
batch_size = 1 # 批处理大小
seq_len = 3 # 序列长度
input_size = 4 # 输入维度
hidden_size = 2 # 隐层维度
cell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size)
# (seq, batch, features)
dataset = torch.randn(seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
hidden = torch.zeros(batch_size, hidden_size)
# 这个循环就是处理seq_len长度的数据
for idx, data in enumerate(dataset):
print('=' * 20, idx, '=' * 20)
print('Input size:', data.shape, data)
hidden = cell(data, hidden)
print('hidden size:', hidden.shape, hidden)
print(hidden)输出结果
==================== 0 ====================
Input size: torch.Size([1, 4]) tensor([[ 1.9129, -0.7440, 0.2329, 1.3065]])
hidden size: torch.Size([1, 2]) tensor([[-0.0790, -0.8957]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward>)
tensor([[-0.0790, -0.8957]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward>)
==================== 1 ====================
Input size: torch.Size([1, 4]) tensor([[-0.6290, -0.2338, -0.2949, 0.3956]])
hidden size: torch.Size([1, 2]) tensor([[ 0.0170, -0.0005]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward>)
tensor([[ 0.0170, -0.0005]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward>)
==================== 2 ====================
Input size: torch.Size([1, 4]) tensor([[-0.6959, 1.0590, -0.6798, 0.6989]])
hidden size: torch.Size([1, 2]) tensor([[0.4216, 0.6813]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward>)
tensor([[0.4216, 0.6813]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward>)How to use RNN
确定几个参数
- input_size和hidden_size: 输入维度和隐层维度
- batch_size: 批处理大小
- seq_len: 序列长度
- num_layers: 隐层数目
- 注 直接调用RNN这个不用循环
- 注:如果使用batch_first: if True, the input and output tensors are provided as:(batch_size, seq_len, input_size)
import torch
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 3
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 2
num_layers = 1
cell = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers)
# (seqLen, batchSize, inputSize)
inputs = torch.randn(seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
out, hidden = cell(inputs, hidden)
print('Output size:', out.shape) # (seq_len, batch_size, hidden_size)
print('Output:', out)
print('Hidden size:', hidden.shape) # (num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
print('Hidden:', hidden)输出结果
Output size: torch.Size([3, 1, 2])
Output: tensor([[[ 0.3689, 0.5982]],
[[ 0.1233, 0.2617]],
[[-0.3517, -0.7246]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward>)
Hidden size: torch.Size([1, 1, 2])
Hidden: tensor([[[-0.3517, -0.7246]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward>)Example: Using RNNCell
Hello –> ohlol
- 首先需要将输入的单词转成向量
one-hot vector - 注意input_size,如下图
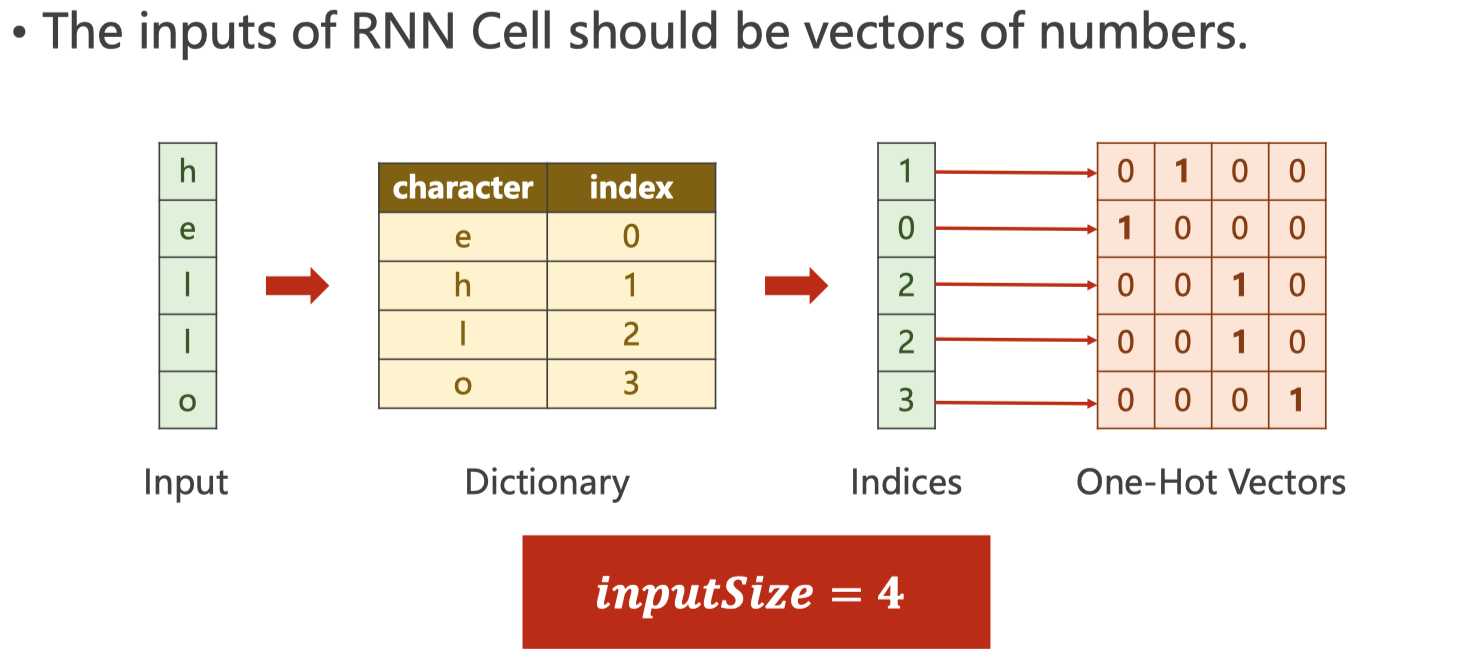
注意交叉熵在计算loss的时候维度关系
这里的hidden是([1, 4]), label是 ([1])
源代码
数据准备
import torch
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
batch_size = 1
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 3, 3] # hello中各个字符的下标
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # ohlol中各个字符的下标
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data] # (seqLen, inputSize)
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(-1, batch_size, input_size)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data).view(-1, 1) # torch.Tensor默认是torch.FloatTensor是32位浮点类型数据,torch.LongTensor是64位整型
print(inputs.shape, labels.shape)输出结果:
torch.Size([5, 1, 4]) torch.Size([5, 1])
构建模型
import torch.nn as nn
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnncell = nn.RNNCell(input_size=self.input_size, hidden_size=self.hidden_size)
def forward(self, inputs, hidden):
hidden = self.rnncell(inputs, hidden) # (batch_size, hidden_size)
return hidden
def init_hidden(self):
return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size)
net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)训练数据
epochs = 15
for epoch in range(epochs):
loss = 0
optimizer.zero_grad()
hidden = net.init_hidden()
print('Predicted string:', end='')
for input, label in zip(inputs, labels):
hidden = net(input, hidden)
# 注意交叉熵在计算loss的时候维度关系,这里的hidden是([1, 4]), label是 ([1])
loss += criterion(hidden, label)
_, idx = hidden.max(dim = 1)
print(idx2char[idx.item()], end='')
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss=%.4f' % (epoch+1, loss.item()))输出结果:
Predicted string:lhlhh, Epoch [1/15] loss=6.8407 Predicted string:lllll, Epoch [2/15] loss=5.2957 Predicted string:lllol, Epoch [3/15] loss=4.9344 Predicted string:lllol, Epoch [4/15] loss=4.7035 Predicted string:oolol, Epoch [5/15] loss=4.4781 Predicted string:oolol, Epoch [6/15] loss=4.2419 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [7/15] loss=3.9733 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss=3.6942 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss=3.4917 Predicted string:ohloo, Epoch [10/15] loss=3.3837 Predicted string:ohloo, Epoch [11/15] loss=3.2953 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss=3.1331 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss=2.9294 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss=2.7344 Predicted string:ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss=2.5680
Example: Using RNN
注意inputs和labels的维度
inputs维度是: (seqLen, batch_size, input_size)labels维度是: (seqLen * batch_size)
注意outputs维度,对应和labels做交叉熵的维度
outputs维度是: (seqLen, batch_size, hidden_size)- 为了能和labels做交叉熵,需要reshape一下: outputs.view(-1, hidden_size)
源代码
数据准备
import torch
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 5
num_layers = 1
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 3, 3] # hello中各个字符的下标
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # ohlol中各个字符的下标
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data] # (seqLen, inputSize)
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
print(inputs.shape, labels.shape)输出结果:
torch.Size([5, 1, 4]) torch.Size([5])
构建模型
import torch.nn as nn
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size, num_layers=1):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=self.input_size, hidden_size=self.hidden_size, )
def forward(self, inputs):
hidden = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, self.batch_size, self.hidden_size)
out, _ = self.rnn(inputs, hidden) # 注意维度是(seqLen, batch_size, hidden_size)
return out.view(-1, self.hidden_size) # 为了容易计算交叉熵这里调整维度为(seqLen * batch_size, hidden_size)
net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)训练模型
epochs = 15
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
# print(outputs.shape, labels.shape)
# 这里的outputs维度是([seqLen * batch_size, hidden]), labels维度是([seqLen])
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted: ', ''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end='')
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.3f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))输出结果:
Predicted: ololl, Epoch [1/15] loss = 1.189 Predicted: ollll, Epoch [2/15] loss = 1.070 Predicted: ollll, Epoch [3/15] loss = 0.976 Predicted: ohlll, Epoch [4/15] loss = 0.883 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [5/15] loss = 0.788 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [6/15] loss = 0.715 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [7/15] loss = 0.652 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss = 0.603 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss = 0.570 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss = 0.548 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss = 0.530 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss = 0.511 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss = 0.488 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss = 0.462 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss = 0.439
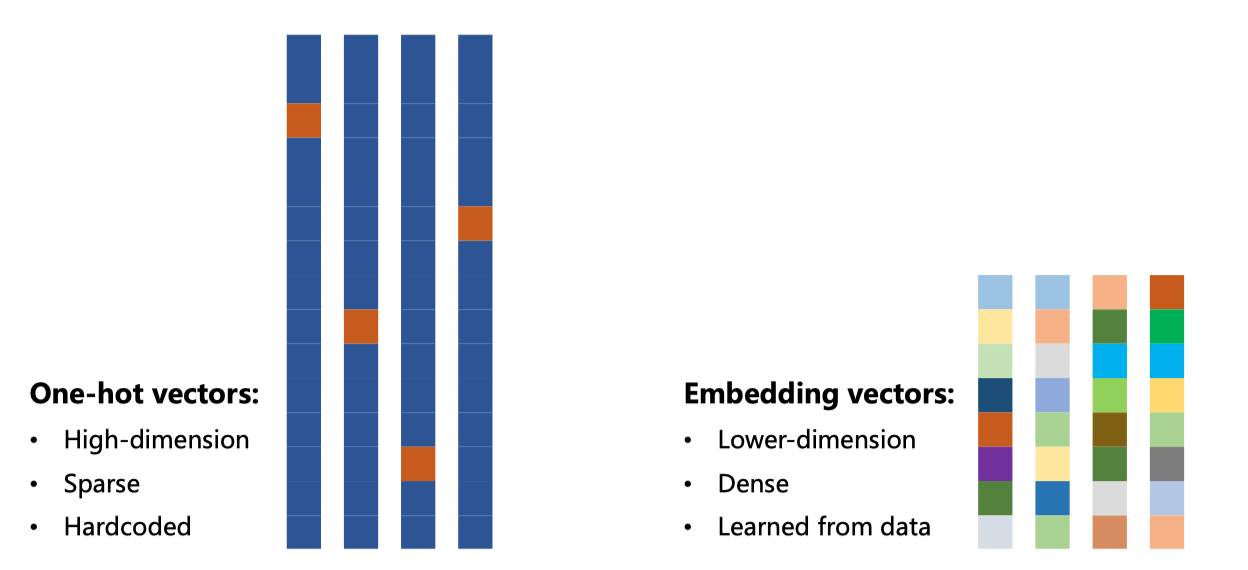
将一个单词变成vector
One-hot encoding of words and characters
one-hot vectors high-dimension –> lower-dimension
one-hot vectors sparse –> dense
one-hot vectors hardcoded –> learn from data
Embedding
源代码
构建模型
import torch.nn as nn
# parameters
num_class = 4
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 8
embedding_size = 10
num_layers = 2
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 5
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
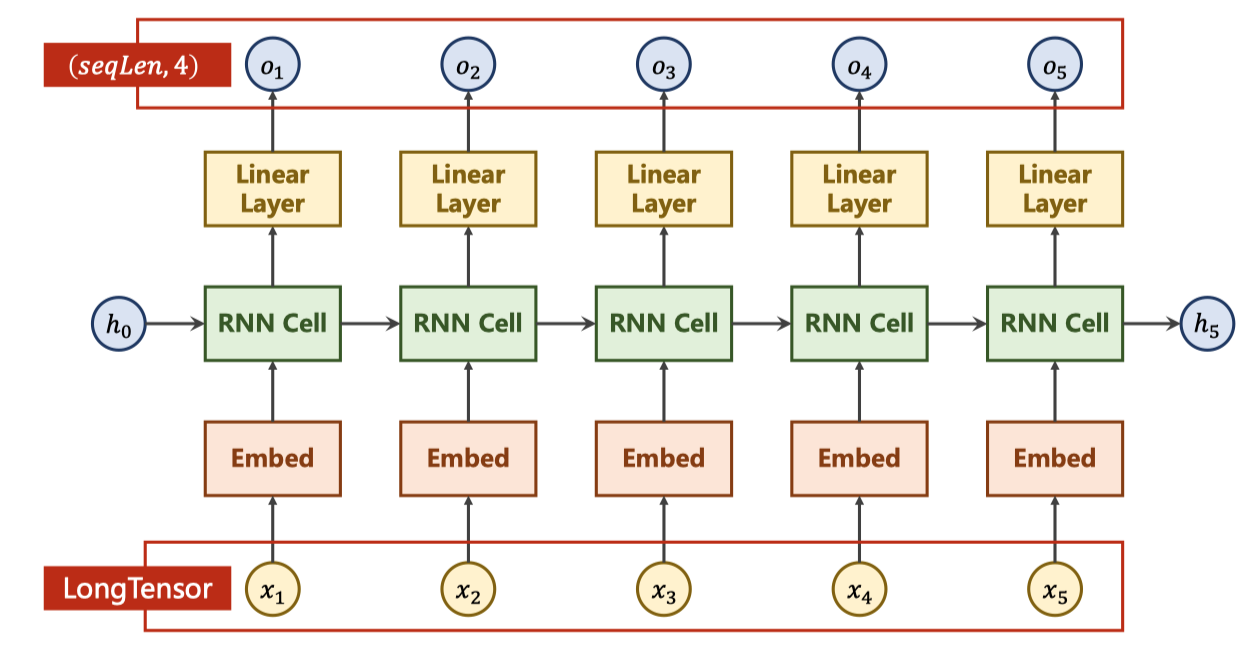
self.emb = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, embedding_size)
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=embedding_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_class)
def forward(self, x):
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers, x.size(0), hidden_size)
x = self.emb(x) # (batch, seqLen, embeddingSize)
x, _ = self.rnn(x, hidden) # 输出(𝒃𝒂𝒕𝒄𝒉𝑺𝒊𝒛𝒆, 𝒔𝒆𝒒𝑳𝒆𝒏, hidden_size)
x = self.fc(x) # 输出(𝒃𝒂𝒕𝒄𝒉𝑺𝒊𝒛𝒆, 𝒔𝒆𝒒𝑳𝒆𝒏, 𝒏𝒖𝒎𝑪𝒍𝒂𝒔𝒔)
return x.view(-1, num_class) # reshape to use Cross Entropy: (𝒃𝒂𝒕𝒄𝒉𝑺𝒊𝒛𝒆×𝒔𝒆𝒒𝑳𝒆𝒏, 𝒏𝒖𝒎𝑪𝒍𝒂𝒔𝒔)
net = Model()
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05)准备数据并训练
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [[1, 0, 2, 2, 3]] # (batch, seq_len)
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # (batch * seq_len)
inputs = torch.LongTensor(x_data) # Input should be LongTensor: (batchSize, seqLen)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data) # Target should be LongTensor: (batchSize * seqLen)
epochs = 15
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted: ', ''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end='')
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss = %.3f' % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))输出结果:
Predicted: ollll, Epoch [1/15] loss = 1.290 Predicted: olooo, Epoch [2/15] loss = 1.071 Predicted: ollol, Epoch [3/15] loss = 0.913 Predicted: ollol, Epoch [4/15] loss = 0.785 Predicted: ollol, Epoch [5/15] loss = 0.660 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [6/15] loss = 0.541 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [7/15] loss = 0.435 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [8/15] loss = 0.343 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [9/15] loss = 0.251 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [10/15] loss = 0.171 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [11/15] loss = 0.121 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [12/15] loss = 0.081 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [13/15] loss = 0.052 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [14/15] loss = 0.036 Predicted: ohlol, Epoch [15/15] loss = 0.025
说明
可以看到使用embedding之后收敛的更快了,说明模型的学习能力变强了



